Rosacea
Overview
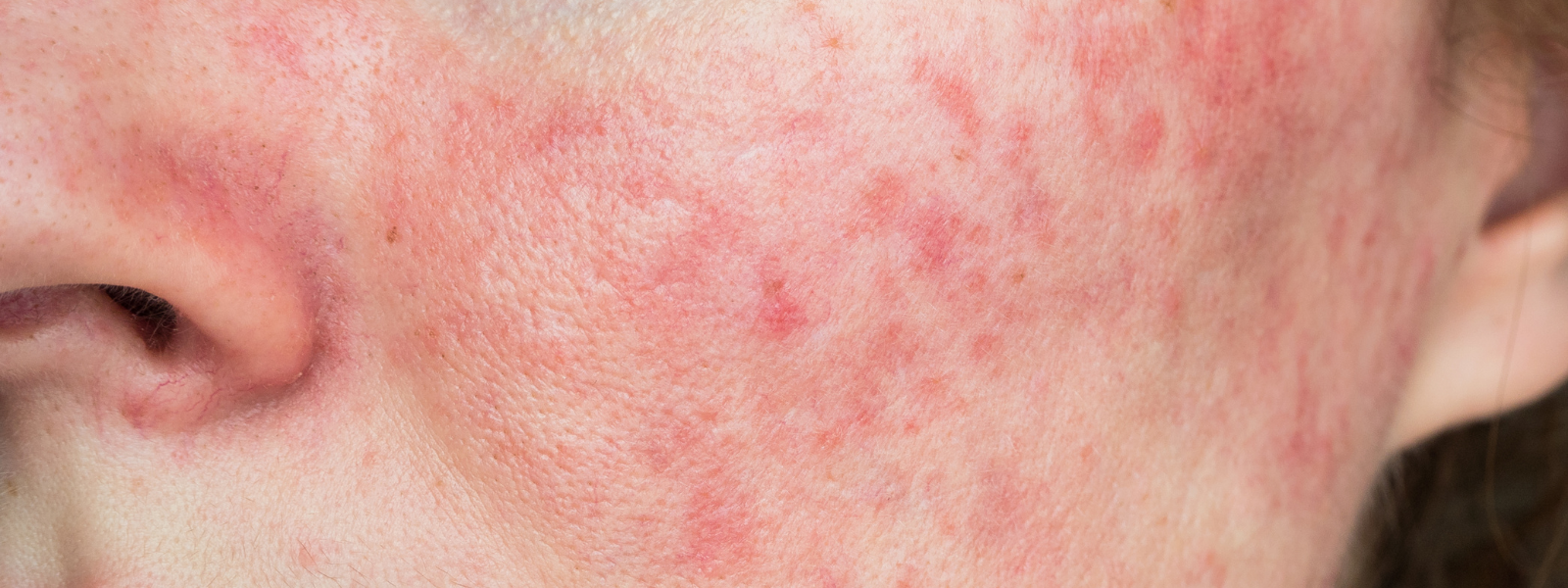
Rosacea Overview
Rosacea is a common skin condition that causes red patches, small red (sometimes pus-filled) bumps or tiny blood vessels visible on the face. Rosacea is occasionally tender or painful and may be embarrassing. More than 3 million people are diagnosed with rosacea each year in the U.S.
Females ages 30 to 60 with fair skin, light hair and blue or green eyes are at a higher risk of developing rosacea. A family history of rosacea may also increase your risk of developing it. Because it is a chronic skin condition that can be effectively treated but not cured, you can experience flare-ups off and on for years or even your entire life.
While researchers do not know the exact cause of rosacea, you may be more likely to develop it if you have a family history of rosacea. Other factors that may trigger a rosacea flare-up include:
- Smoking
- Spicy foods
- Hot beverages
- Stress and emotions
- Alcoholic beverages
- Extreme temperatures
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight or wind
- Medications that dialate blood vessels
Symptoms
Rosacea Symptoms
Sometimes people may confuse rosacea with natural ruddiness, acne or other skin conditions. Common signs of rosacea include:
Ocular rosacea can cause dry, red, irritated eyes and swollen eyelids. Sometimes ocular rosacea can happen even before rosacea appears on your face.
Diagnosis
Rosacea Diagnosis
It is not uncommon to confuse rosacea with acne or other skin problems. Your doctor will ask about your and your family’s medical history and examine your skin. Although no lab work is necessary to diagnose rosacea, your doctor may order tests to rule out other skin conditions or to help determine the cause of your rosacea.
Treatments
Rosacea Treatments
Because rosacea is not curable, treatment controls the symptoms with medications and therapy.
Medications
Topical creams or gels
Applied to the affected area of mild-to-moderate rosacea
Sunscreen
An integral part of all rosacea treatment
Oral antibiotics
Can help control the bumps and pimples associated with moderate to severe rosacea
Oral acne medicines
Your doctor may prescribe oral acne medications in severe rosacea that does not respond well to other treatments
Lasers
Lasers can be used to get rid of the dilated blood vessels and redness on the face.
Because rosacea is chronic, various treatments may be necessary throughout your life whenever you experience flare-ups. You may be able to reduce flare-ups by adjusting your skincare routine.
- Identify and avoid triggers
- Be gentle when cleansing your skin
- Avoid products that contain alcohol
- Moisturize your face often
- Wear a hat and scarf to protect your skin from sun, wind, heat and cold
- Protect your skin, especially your face, with a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher (applied after any topical treatments your doctor has prescribed)
Specialists

